Dental discomfort can creep in quietly and disrupt your daily routine. A simple sip of cold water, a bite into an ice cream cone, or brushing your teeth can suddenly become painful. But is that sharp twinge in your mouth a sign of sensitivity or something more concerning, like a cavity?
Dr. Jahnavi Patel, Managing director at Dentafix Dental Clinic and an accomplished Dental Expert in South Bopal, Ahmedabad, shares:
“Many patients come in confused between a cavity and tooth sensitivity. Both conditions can feel similar at first, but they stem from different causes and need very different treatments. Spotting the signs early can save you a lot of discomfort and money in the long run.”

Globally, over 2.4 billion people suffer from untreated dental caries (cavities), making it one of the most prevalent health issues, according to the WHO. In India alone, about 60-80% of children and 85-90% of adults are affected by dental caries and sensitivity issues. This shows just how vital it is to understand the root cause of your dental pain.
Let’s help you decode the difference between a sensitive tooth vs cavity.
What Is Tooth Sensitivity?
Tooth sensitivity, medically known as dentin hypersensitivity, happens when the protective enamel of the tooth wears down, exposing the underlying dentin and nerve endings.
Here are the common causes of tooth sensitivity:
Worn enamel: Frequent consumption of acidic foods, aggressive brushing, or using hard-bristled toothbrushes can erode enamel.
Gum recession: When gums recede, they expose the root surface, which is more sensitive.
Cracked teeth: These can expose inner layers and increase sensitivity.
Teeth grinding (bruxism): This habit can wear down enamel over time.
Whitening products or acidic mouthwashes: Some oral care products can trigger temporary sensitivity.
Patients often describe the pain as sudden, sharp, and usually triggered by:

Cold or hot food and drinks
- Sweet or acidic items
- Brushing or flossing
Dr. Jahnavi Patel, a compassionate Preventive Dentistry Specialist in South Bopal, Ahmedabad, advises,
“Sensitivity is usually a signal that your teeth are trying to warn you. It’s often reversible and manageable, especially when diagnosed early. But ignoring it can pave the way for more serious issues.”
A tiny hole can cause big problems… Let’s look deeper.
What Is a Cavity?
A cavity is a form of tooth decay caused by the gradual destruction of tooth enamel due to plaque and bacteria. If not treated, it can progress into the deeper layers of the tooth, potentially requiring extensive treatment like root canals or extractions.
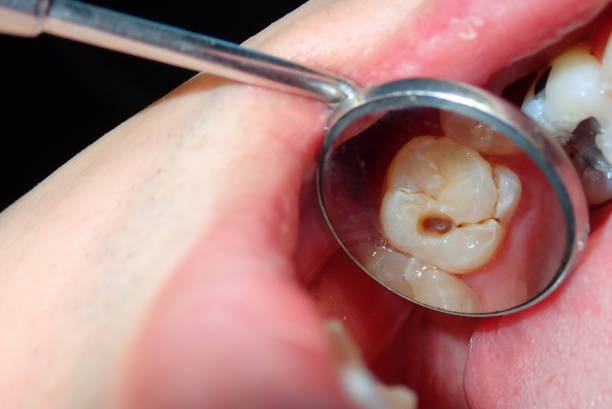
Here’s how cavities typically form:
Plaque buildup: A sticky film of bacteria that feeds on sugar and releases acids.
Acid attack: These acids demineralize and weaken the enamel.
Decay penetration: Once the enamel is breached, decay spreads into the dentin and pulp.
Common signs of a cavity:

- Persistent or dull toothache
- Pain when biting down
- Black, brown, or white spots on the tooth
- Visible holes or pits
- Sensitivity that lingers even after the trigger is gone
Dr. Jahnavi Patel, a meticulous Restorative Dentistry Consultant in South Bopal, Ahmedabad, explains,
“Cavities can silently progress without causing pain at first. That’s why regular dental check-ups are critical. Early-stage decay can often be treated with simple fillings, avoiding more complex procedures later.”
Confused whether it’s just sensitivity or something more serious? Here’s how to tell.
Key Differences – Sensitive Tooth vs Cavity
Understanding the difference between cavity and sensitivity can be challenging, but comparing them side by side helps:
|
Feature |
Tooth Sensitivity |
Cavity Pain |
|
Trigger |
Cold, heat, sweetness, pressure |
Sweet, heat, chewing, often continuous |
|
Pain Duration |
Brief, sharp discomfort |
Lingering pain or persistent ache |
|
Location |
Often generalized |
Usually localized to one tooth |
|
Visual Clues |
None or gum recession |
Visible pits, discoloration |
|
Response to Stimuli |
Immediate and short-lived |
Gets worse over time |
Understanding these differences can help you decide when to seek dental advice. However, self-diagnosis isn’t foolproof.
Still unsure? You don’t need to figure it out alone. Consult a dental professional to assess the root cause and get tailored advice for effective relief.
So how do dental experts get to the bottom of your tooth pain? Let’s find out.
How Dentists Diagnose the Issue
Dentists use a combination of clinical expertise and diagnostic tools to identify whether you’re dealing with sensitivity or decay.
Here’s what a standard dental evaluation might include:
Visual Examination: Checking for visible signs like pits, cracks, or enamel erosion.
Tactile Test: Using a dental explorer to detect soft or sticky spots indicating decay.
Cold Stimulus Test: Applying cold air or water to isolate sensitivity.
Percussion Test: Tapping teeth gently to identify deep infections.
X-rays: To detect cavities between teeth or below the surface.
Dr. Jahnavi Patel, a detail-oriented Dental Implant Specialist in South Bopal, Ahmedabad, says:
“An accurate diagnosis is the foundation of effective treatment. At our clinic, we combine careful physical examination with digital radiographs to identify even the smallest areas of concern. This ensures our patients receive the right treatment the first time.”
Next, let’s talk solutions.
Treatment Options
For Sensitivity

If your discomfort stems from dental sensitivity, treatment focuses on strengthening enamel and protecting the exposed dentin:
Desensitizing toothpaste: These help block nerve signals from the tooth surface.
Fluoride varnishes: Strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity.
Bonding agents: Coat exposed areas to prevent stimuli from reaching the nerves.
Mouthguards: For bruxism-related sensitivity, especially at night.
For Cavities
When it’s confirmed to be a cavity, the solution is to remove decay and restore the tooth structure:
Fillings: Composite or amalgam fillings for small-to-moderate decay.
Inlays/Onlays: For more extensive damage without reaching the root.
Root canal: If the pulp is infected, this removes the nerve tissue and seals the tooth.
Crowns: In severe decay cases, to protect and restore the tooth structure.
Don’t wait until it worsens. Early action makes a big difference.
Experiencing pain that doesn’t seem to go away? Schedule an appointment with a dentist to identify the underlying issue and get expert treatment before it escalates.
Maintaining good oral health habits can help avoid both cavities and sensitivity.
Prevention Tips for Both Conditions
Here are some proven ways to protect your teeth:
Brush gently with a soft-bristled brush: Avoid aggressive brushing to protect enamel and gums.
Use fluoride toothpaste: Strengthens enamel and helps resist decay.
Limit sugary and acidic foods: These erode enamel and feed harmful bacteria.
Floss daily: Removes plaque and food particles from between teeth.
Drink water after meals: Helps rinse away food acids and sugars.
Regular dental visits: Early detection prevents serious issues.
Wear a mouthguard if you grind teeth: Prevents enamel wear.
Prevention is key—but knowing when to seek help is equally crucial.
When to See a Dentist
While occasional sensitivity might not be alarming, persistent or worsening symptoms should not be ignored.
Visit a dentist if:
- You experience sharp pain frequently
- The pain lingers after the trigger is gone
- There’s visible discoloration or holes
- You have swelling or bleeding gums
- You’ve had sensitivity for more than a week
Still have questions? You’re not alone. Let’s clear up common doubts.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Can a sensitive tooth turn into a cavity?
Are cavities always visible or painful?
Will desensitizing toothpaste help if I have a cavity?
How long does it take for a cavity to form?
What are the early signs of a cavity?
Dealing with ongoing tooth discomfort? Connect with a qualified dentist today for a personalized evaluation and long-term relief.
References:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10946-cavities
Disclaimer:
This content is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional dental advice. Please consult a qualified dentist for diagnosis and treatment of any dental condition.